Accelerated TMS - moving quickly into the future of depression treatment
- Cadiz Salazar
- Jan 29
- 2 min read
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is evolving rapidly, with a new focus on accelerated protocols to treat depression more quickly and effectively. Here's an overview of the key points:

Accelerated TMS: A Promising Development
Accelerated TMS aims to reduce treatment duration and improve response time for patients with depression. This approach is gaining traction due to its potential to provide faster relief.
How TMS Works
TMS uses magnetic fields to stimulate specific brain regions, particularly the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), which is involved in mood regulation.
Stimulation Frequencies
- High-frequency TMS (≥5 Hz): Generally considered excitatory
- Low-frequency TMS (typically 1 Hz): Often thought to be inhibitory
However, this simple categorization may be an oversimplification, as neuroimaging studies have shown mixed results regarding the directional effects of different frequencies.
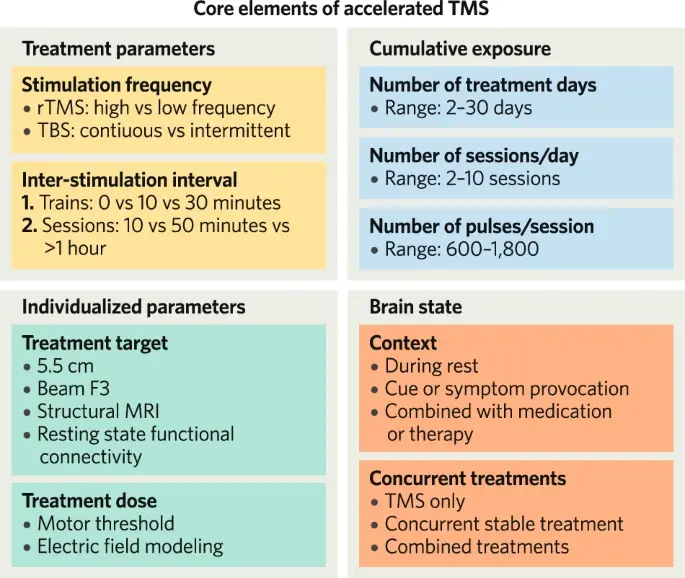
Emerging Protocols
1. Intermittent Theta Burst Stimulation (iTBS): A more rapid and potent form of TMS
2. Accelerated Protocols**: Involve condensed treatment schedules with high-frequency bursts
These new approaches aim to entrain endogenous brain rhythms, potentially leading to greater neuroplasticity and faster symptom reduction.
Promising Results
Recent trials using accelerated iTBS protocols have reported remission rates up to 90% in patients with major depressive disorder (MDD).
Future Directions
Researchers are exploring ways to optimize TMS protocols, including:
- Personalized targeting based on individual brain connectivity
- Combining TMS with other therapies for enhanced effects
- Investigating its potential for treating other psychiatric disorders beyond depression
Accelerated TMS represents an exciting frontier in depression treatment, offering hope for faster and more effective relief for patients struggling with this challenging condition.
Citations:


Comentários